Chitosan Oligosaccharide (Crustacean)
Oligosaccharide Chitosan - Derived from Crustacean
Water Soluble / Medium-High Deacetylation / Very Low Molecular Weight
Product number: CO-101211
CAS Number: 9012-76-4
Chitosan synonym: Deacetylated chitin, Poly(D-glucosamine)
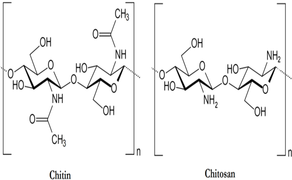
Properties
Deacetylation: 86.5%
Molecular Weight (kDa): <3
Solubility: Water Soluble
Starting material: Crustacean - Snow Crab Shell
Appearance: brown
Particle Mesh: NLT 98% through 160 mesh
US $1.93 Per Gram .... prices are lower with larger amounts (1Kg+) purchased.
Minimum Order Quantity: 100 grams
For other payment methods, quantities, or more information…
Oligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide, a sugar, is a saccharide polymer containing a small number monosaccharides (simple sugars). An oligosaccharide commonly refers to a carbohydrate polymer whose molecules are composed of a relatively small number of monosaccharide units. The parameters for an oligosaccharide vary, however they are typically counted as any sugar with between 3 and 9 monosaccharide units. Oligosaccharides are formed when two or more monosaccharides join together by O-glycosidic bonds. Examples include sucrose, lactose and maltose. Specific enzymes are used to catalyze the glycosidic bonds in oligosaccharides and each sugar must be specific to each enzyme used for each new glycosidic bond.
Speed up R&D and its documentation
Save R&D time and costs
Increase chances of approval and commercialization

